Enterprise Documentation
The Circuit Breaker
Document updated on Dec 5, 2022
About this feature
| Namespace | qos/circuit-breaker |
|---|---|
| Log prefix | [BACKEND: /foo][CB] |
| Scope | backend |
| Source | krakend/krakend-circuitbreaker |
The Circuit Breaker is a straightforward state machine in the middle of the request and response that monitors all your backend failures. When they reach a configured threshold, the circuit breaker will prevent sending more traffic to a failing backend alleviating its pressure under challenging conditions.
When KrakenD demands more throughput than your actual API stack can deliver properly, the Circuit Breaker mechanism will detect the failures and prevent stressing your servers by not sending requests that are likely to fail. It is also helpful for dealing with network and other communication problems by preventing too many requests from dying due to timeouts, etc.
Circuit breaker configuration
The Circuit Breaker is available in the namespace qos/circuit-breaker inside the extra_config key. The following configuration is an example of how to add circuit breaker capabilities to a backend:
{
"endpoints": [
{
"endpoint": "/myendpoint",
"method": "GET",
"backend": [
{
"host": [
"http://127.0.0.1:8080"
],
"url_pattern": "/mybackend-endpoint",
"extra_config": {
"qos/circuit-breaker": {
"interval": 60,
"timeout": 10,
"max_errors": 1,
"name": "cb-myendpoint-1",
"log_status_change": true
}
}
}
]
}
]
}
The attributes available for the configuration are:
Fields of Circuit Breaker
| Time window where the errors count, in seconds. |
| Whether to log the changes of state of this circuit breaker or not. Defaults to false |
| The consecutive number of errors within the interval window to consider the backend unhealthy. An error is any response without a success (20x) status code or no response. |
| A friendly name to follow this circuit breaker’s activity in the logs. Example: "cb-backend-1" |
| For how many seconds the circuit breaker will wait before testing again if the backend is healthy. |
How the Circuit Breaker works
It’s easy to picture the state of the circuit breaker as an electrical component, where an open circuit means no flow of electricity between the ends, and a closed one normal flow:
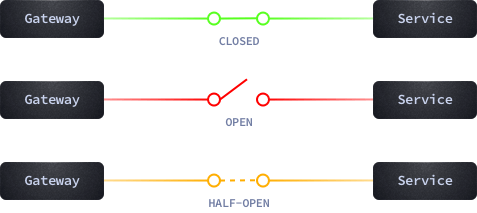
The Circuit Breaker starts with the CLOSED state, meaning the electricty can flow to the backends as they are considered healthy (innocent until proven guilty).
Then the component watches the state of the connections with your backend(s), with a tolerance to consecutive failures (max_errors) during a time interval (interval). it stops all the interaction with the backend for the next N seconds (the timeout). We call this state OPEN.
After waiting for this time window, the state changes to HALF-OPEN and allows a single connection to pass and test the system again. At this stage:
- If the test connection fails, the state returns to “open” and the circuit breaker will wait N seconds again to test it again.
- If it succeeds, it will return to the “closed “state, and the system is considered healthy.
This is the way the states change:
| Circuit Breaker transitions |
|---|
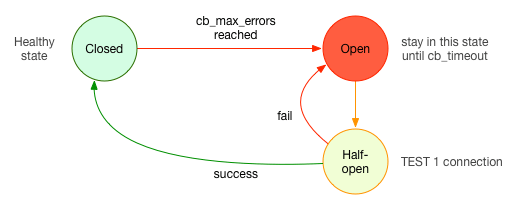 |
CLOSED: In the initial state, the system is healthy and sending connections to the backend.OPEN: When a consecutive number of supported errors from the backend (max_errors) is exceeded, the system changes toOPEN, and no further connections are sent to the backend. The system will stay inOPENstate for N seconds ( thetimeout).HALF-OPEN: After the timeout, it changes to this state and allows one connection to pass. If the connection succeeds, the state changes toCLOSED, and the backend is considered to be healthy again. But if it fails, it switches back toOPENfor another timeout.
Definition of failure
A failure that counts for the circuit breaker could be anything that prevents having a successful connection with the service. There is a small difference in behavior when you use the circuit breaker with no-op encoding vs. the rest of the encodings.
Regardless of the encoding, the Circuit Breaker will react to:
- Network or connectivity problems
- Security policies
- Timeouts
- Components in the list returning errors or having issues:
- Proxy rate limit (
qos/ratelimit/proxy) - Lua backend scripts (
modifier/lua-backend) - CEL in the backend (
validation/cel) - Lambda (
backend/lambda) - AMQP or PubSub issues
- Proxy rate limit (
In addition, when you work with json, or any other encoding different than no-op, the gateway also checks the HTTP responses back from the backend and marks as failures:
- Status codes different than
200or201(including client credentials) - Decoding issues
- Martian issues