Document updated on Jan 31, 2023
Auditing KrakenD API Gateway Configurations
The krakend audit command is a rule evaluation tool that checks configuration files written in any of its supported formats and returns practical security recommendations. It is designed to raise basic red flags and provide essential advice on your configuration. The output of the configuration and classification is inspired by the CIS Benchmarks.
The tool displays practical and helpful information, including (but not limited to) misconfigurations opening the door to vulnerabilities, presence/absence of key components, dangerous flags or combinations, conflicting declarations, and statistics (planned), to put a few examples.
Audit vs Check
The audit command is complementary to the check command. Still, instead of focusing on the configuration file structure and linting, it evaluates the logic at a different stage. The command executes after parsing the configuration, using a summarized tree of the final recognized components and flags loaded. It does not has access to the values of the properties (but check does). For instance, if you write a jwk_url to validate tokens, audit does not know if you are using HTTPS or HTTP or which domain, but it does see if you have disable_jwk_security, which is dangerous in production.
The purpose of the audit command is to add extra checks in your automated CI pipeline to have safer deployments.
Audit configuration
The audit command has the following options:
Usage of KrakenD audit
$krakend audit --help
╓▄█ ▄▄▌ ╓██████▄µ
▐███ ▄███╨▐███▄██H╗██████▄ ║██▌ ,▄███╨ ▄██████▄ ▓██▌█████▄ ███▀╙╙▀▀███╕
▐███▄███▀ ▐█████▀"╙▀▀"╙▀███ ║███▄███┘ ███▀""▀███ ████▀╙▀███H ███ ╙███
▐██████▌ ▐███⌐ ,▄████████M║██████▄ ║██████████M███▌ ███H ███ ,███
▐███╨▀███µ ▐███ ███▌ ,███M║███╙▀███ ███▄```▄▄` ███▌ ███H ███,,,╓▄███▀
▐███ ╙███▄▐███ ╙█████████M║██▌ ╙███▄`▀███████╨ ███▌ ███H █████████▀
`` `'`
Version: 2.5
Audits a KrakenD configuration.
Usage:
krakend audit [flags]
Examples:
krakend audit -i 1.1.1,1.1.2 -s CRITICAL -c krakend.json
Flags:
-c, --config string Path to the configuration file
-f, --format string Inline go template to render the results (default "{{ range .Recommendations }}{{.Rule}}\t[{{colored .Severity}}] \t{{.Message}}\n{{ end }}")
-h, --help help for audit
-i, --ignore string List of rules to ignore (comma-separated, no spaces)
-I, --ignore-file string Path to a text-plain file containing the list of rules to exclude
-s, --severity string List of severities to include (comma-separated, no spaces) (default "CRITICAL,HIGH,MEDIUM,LOW")The simplest version of the command requires the path to the configuration file only, and outputs any problems found:
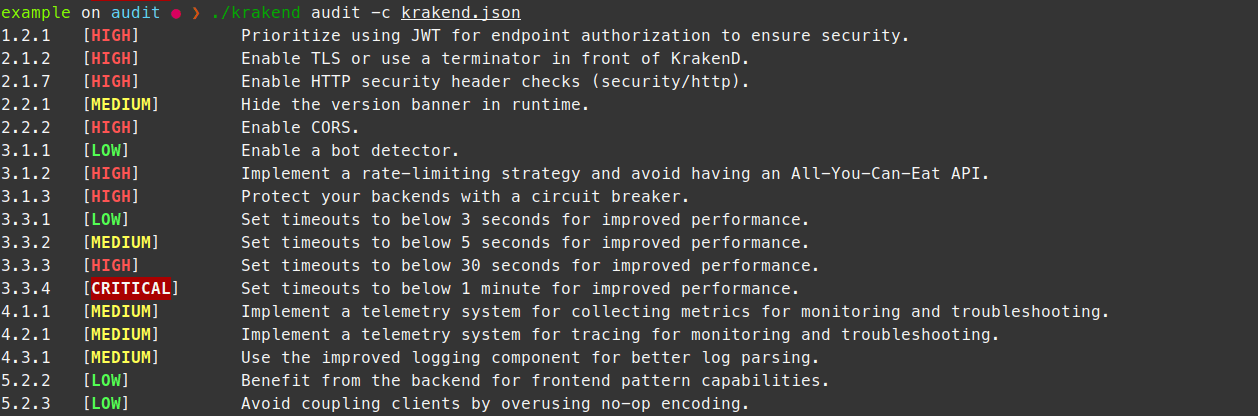
Audit configuration
$krakend audit -c krakend.json
1.2.1 [HIGH] Prioritize using JWT for endpoint authorization to ensure security.
2.2.1 [MEDIUM] Hide the version banner in runtime.
3.3.4 [CRITICAL] Set timeouts to below 1 minute for improved performance.
5.2.3 [LOW] Avoid coupling clients by overusing no-op encoding.It also accepts different flags to customize its behavior:
--severity,-s: Severity requirements--ignore,-i: Rules to ignore (inline)--ignore-file,-I: Rules to ignore (from file)--format,--f: Format of the output (Go template)
More details of the flags below.
Configuring the audit severity
By default, the audit command will include all severity levels. However, you can choose through the --severity flag which groups you want to be printed in the console, separated by commas. The list is:
CRITICALHIGHMEDIUMLOW
When the --severity is not defined, KrakenD uses --severity CRITICAL,HIGH,MEDIUM,LOW. You can use a comma separated string (no spaces) with all the severities you want to print. For instance, using the same example we had above, to filter by the most severe problems you would type:
Term
$krakend audit --severity CRITICAL,HIGH -c krakend.json
1.2.1 [HIGH] Prioritize using JWT for endpoint authorization to ensure security.
3.3.4 [CRITICAL] Set timeouts to below 1 minute for improved performance.Excluding security audit rules
The outputted security recommendations by the command are generic to any installation and might not apply to your setup, or you might disagree with our assigned severity. You can exclude future checking of any specific audit rules by passing a list or creating an exception file. To do that, use the --ignore flag passing a comma-separated list (no spaces) with all the ignore rules or a --ignore-file with the path to an ignore file.
All rules must have the numeric format x.y.z.
For the inline option, you could do the following:
Ignore rules 1.2.3 and 4.5.6
$krakend audit --ignore=1.2.3,4.5.6 -c krakend.jsonFor the option of an ignore file, you should create a plain text file with one rule per line. You can place this file anywhere and it does not require a specific extension or name. However, if it is not in the KrakenD workdir (/etc/krakend/), you must specify its relative or absolute path:
Content of the ignore file
$cat .audit_ignore
1.2.3
4.5.6And then calling it with:
Ignore rules 1.2.3 and 4.5.6
$krakend audit --ignore-file=.audit_ignore -c krakend.jsonCustomizing the output
Finally, you can choose the format of the output according to your needs by injecting a Go template using the -f flag. The flag expects an inline template.
The default template, as shown in the screenshot, applies the following go template:
{{ range .Recommendations }}{{.Rule}}\t[{{colored .Severity}}]\t{{.Message}}\n{{ end }}
As the ouput is processed using a template, you can inject anything you like. For instance, the example below generates a TOML file into recommendations.toml.
Custom output
$krakend audit -f '{{range .Recommendations}}
[[recommendation]]
rule = "{{.Rule}}"
message = "{{.Message}}"
severity = "{{.Severity}}"
{{end}}' > recommendations.tomlOr the JSON format is even easier to write:
JSON output
$krakend audit -f '{{ marshal . }}' > recommendations.jsonAs you can see, the templates use a series of variables and functions, as follows:
.Recommendations: An array with all the recommendations, where each recommendation has the following structure:.Rule: The identifier of this rule. E.g.,1.1.1.Message: A short message describing the recommendation..Severity: The level of severity for this recommendation
In addition, you can use two functions:
coloredto add colors to the severity ({{colored .Severity}}) when the output is in a terminalmarshalto return a JSON representation of the variable. E.g.,{{ marshal . }}
Audit recommendations
The following is the list of recommendations you can find in the audit results. The recommendations are classified using a numeric code with the format x.y.z. You can use this rule identifier to exclude the rules during its checking, as explained above.
1. AuthZ and AuthN
Recommendations for implementations of authorization or authentication to a more secure access control.
1.1 Authentication
Recommendations for authentication issues only
- Recommendation
-
1.1.1Implement more secure alternatives than Basic Auth to protect your data. - Severity
- HIGH
- Rationale
- Basic Auth is an insecure authentication method and is considered deprecated. It does not offer expiration mechanisms and can be hacked easily.
- Recommendation
-
1.1.2Implement stateless authorization methods such as JWT to secure your endpoints as opposed to using API keys. - Severity
- MEDIUM
- Rationale
- API keys can be easily compromised and do not offer expiration mechanisms. Using JWT for stateless authorization ensures a secure and efficient way to authenticate and authorize users.
1.2 Authorization
Recommendations for authorization issues only (token validation)
- Recommendation
-
1.2.1Prioritize using JWT for endpoint authorization to ensure security. - Severity
- HIGH
- Rationale
- Properly securing endpoints through authorization is crucial for the security of your API. JWT is a recommended method for stateless authorization, as it ensures that the token is valid and has not been tampered with. Add JWT validation
2. HTTP transport
This section covers recommendations for securing the HTTP transport, including TLS and securing HTTP headers.
2.1 TLS
Recommendations for securing the use of TLS, ensuring that insecure connections are not allowed, that TLS is enabled and configured properly, and that strong cryptographic ciphers are used.
- Recommendation
-
2.1.1Only allow secure connections (avoid insecure_connections). - Severity
- HIGH
- Rationale
- This recommendation ensures that KrakenD is configured to only allow secure connections using TLS. This helps to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks and other forms of eavesdropping. Disallow insecure connections
- Recommendation
-
2.1.2Enable TLS or use a terminator in front of KrakenD. - Severity
- HIGH
- Rationale
- This recommendation ensures that KrakenD is either configured to use TLS or that a terminator is used in front of KrakenD to handle the encryption. This helps to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks and other forms of eavesdropping. Enable TLS
- Recommendation
-
2.1.3TLS is configured but its disable flag prevents from using it - Severity
- CRITICAL
- Rationale
- This recommendation ensures that TLS configuration does not have a disable flag to override it. Without this, communication between clients and KrakenD would be unencrypted and susceptible to eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks. Remove
disable
- Recommendation
-
2.1.7Enable HTTP security header checks (security/http). - Severity
- HIGH
- Rationale
- It is important to enable HTTP security header checks to ensure that your system is protected against common web-based attacks such as cross-site scripting (XSS) and clickjacking. Enable http security
- Recommendation
-
2.1.8Avoid clear text communication (h2c). - Severity
- HIGH
- Rationale
- The h2c flag uses HTTP/2 in clear text. Use HTTP/2 over TLS instead (no flag declaration). Disable h2c
- Recommendation
-
2.1.9Establish secure connections in internal traffic (avoid insecure_connections internally). - Severity
- LOW
- Rationale
- This recommendation ensures that KrakenD is configured to only allow secure connections using TLS. This helps to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks and other forms of eavesdropping. Disallow insecure connections
2.2 Headers and parameters
Recommendations for HTTP headers configuration and parameter forwarding
- Recommendation
-
2.2.1Hide the version banner in runtime. - Severity
- MEDIUM
- Rationale
- It is important to hide the KrakenD version banner in order to prevent attackers from identifying vulnerabilities in your specific version of the software. Add the flag hide_version_header.
- Recommendation
-
2.2.2Enable CORS. - Severity
- HIGH
- Rationale
- Cross-Origin Resource Sharing allows secure communication between different domains, which is crucial for protecting against cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks. Enable CORS
- Recommendation
-
2.2.3Avoid passing all input headers to the backend. - Severity
- HIGH
- Rationale
- Enabling the wildcard pollutes your backends and opens the door to malicious attackers to get through the gateway and scan your backend for vulnerabilities. Avoid wildcard headers
- Recommendation
-
2.2.4Avoid passing all input query strings to the backend. - Severity
- HIGH
- Rationale
- Enabling the wildcard pollutes your backends and opens the door to malicious attackers to get through the gateway and scan your backend for vulnerabilities. Avoid wildcard query strings
- Recommendation
-
2.2.5Avoid exposing gRPC server without services declared. - Severity
- LOW
- Rationale
- You are opening a gRPC server in the gateway that has no possible use, and therefore enabling it is an open door with no benefits.
2.3 Transport
Recommendations for HTTP transport
- Recommendation
-
2.3.1Limit the amount of cacheable content. - Severity
- MEDIUM
3. Traffic Management
Recommendations for a better control of traffic and avoid disruptions
3.1 QoS
Recommendations for ensuring Quality of Service
- Recommendation
-
3.1.1Enable a bot detector. - Severity
- LOW
- Rationale
- Enabling a Bot detector can prevent unwanted crawling, and impacting performance for legitimate users. Enable a bot detector
- Recommendation
-
3.1.2Implement a rate-limiting strategy and avoid having an All-You-Can-Eat API. - Severity
- HIGH
- Rationale
- Implementing a rate-limiting strategy can prevent a single user or service from overloading your API and impacting performance for other users. It also helps to prevent abuse and unwanted usage patterns. Add throttling
- Recommendation
-
3.1.3Protect your backends with a circuit breaker. - Severity
- HIGH
- Rationale
- Implementing a circuit breaker can protect your backends from being overwhelmed by requests in case of a service failure or unexpected traffic spike, by automatically stopping requests from being sent to the backend until the issue is resolved. Add a circuit breaker
3.2 Retry policies
Retry policies to reconnect to key services behind KrakenD (future release)
3.3 Timeouts
Recommendations for healthy timeouts and avoid overloading the system
- Recommendation
-
3.3.1Set timeouts to below 3 seconds for improved performance. - Severity
- LOW
- Rationale
- Having short timeouts can help prevent slow requests from holding up the system and causing delays for other users. A timeout of 3 seconds or less is considered high enough and should be sufficient for most use cases. Lower the timeout
- Recommendation
-
3.3.2Set timeouts to below 5 seconds for improved performance. - Severity
- MEDIUM
- Rationale
- Having medium-length timeouts can help prevent slow requests from holding up the system and causing delays for other users. A timeout of 5 seconds or more is considered high and should not be used in most of the cases. Lower the timeout
- Recommendation
-
3.3.3Set timeouts to below 30 seconds for improved performance. - Severity
- HIGH
- Rationale
- Having long timeouts can help prevent slow requests from holding up the system and causing delays for other users. A timeout of 30 seconds or more is considered very high. Lower the timeout
- Recommendation
-
3.3.4Set timeouts to below 1 minute for improved performance. - Severity
- CRITICAL
- Rationale
- Having timeouts set above 1 minute can lead to security vulnerabilities such as denial of service attacks. It’s important to ensure that your timeouts are always low to prevent these types of issues. Lower the timeout
4. Telemetry
Recommendations for having full visibility of the gateway and underlying services activity.
4.1 Metrics
Recommendations for the use of metrics.
- Recommendation
-
4.1.1Implement a telemetry system for collecting metrics for monitoring and troubleshooting. - Severity
- MEDIUM
- Rationale
- Having a telemetry system in place is crucial for monitoring the performance and health of your KrakenD service. It allows you to track metrics such as request count, response time, and error rate. Add metrics
- Recommendation
-
4.1.3Avoid duplicating telemetry options to prevent system overload. - Severity
- HIGH
- Rationale
- Having multiple telemetry options enabled can cause an overload on the system and make it harder to monitor your metrics. Ensure that you only have the necessary options enabled and that they are not duplicated.
4.2 Tracing
Recommendations for the use of traces
- Recommendation
-
4.2.1Implement a telemetry system for tracing for monitoring and troubleshooting. - Severity
- MEDIUM
- Rationale
- Implementing a telemetry system, such as OpenTracing, allows for better tracking and debugging of requests and can help identify issues or performance bottlenecks. Add tracing
4.3 Logging
Recommendations for logging activity and best practices
- Recommendation
-
4.3.1Use the improved logging component for better log parsing. - Severity
- MEDIUM
- Rationale
- The improved logging component allows for better parsing of logs, making it easier to identify and troubleshoot issues. This is a recommended configuration to have in place. Add logging
5. API Gateway
General recommendations to have a better API gateway definition
5.1 Routing
Recommendations for routing and endpoint structure
- Recommendation
-
5.1.1Follow a RESTful endpoint structure for improved readability and maintainability. - Severity
- LOW
- Rationale
- RESTful endpoint structure is a best practice for API design and makes it easier for developers to understand and consume your API. Make sure that your endpoints are organized in a logical and consistent manner, and that they follow the standard CRUD operations. Remove
disable_rest
- Recommendation
-
5.1.2Disable the /__debug/ endpoint for added security. - Severity
- LOW
- Rationale
- The
/__debug/endpoint is a special endpoint that is used for debugging and testing purposes, and despite is considered safe to use in production, it’s not necessary in production environments. Remove the debug endpoint.
- Recommendation
-
5.1.3Disable the /__echo/ endpoint for added security. - Severity
- LOW
- Rationale
- The
/__echo/endpoint is a special endpoint that is used for debugging and testing purposes. It’s not necessary in production environments. Remove the echo endpoint.
- Recommendation
-
5.1.4Declare explicit endpoints instead of using wildcards. - Severity
- LOW
- Rationale
- Using wildcard endpoints might be very convenient to maintain less endpoints, but it opens the door to having zombie APIs and endpoints. Zombie APIs are those forgotten entries that you are not aware they are published. Remove wildcards.
- Recommendation
-
5.1.5Declare explicit endpoints instead of using /__catchall. - Severity
- MEDIUM
- Rationale
- Although this endpoint might be super-useful, keep in mind that, generally speaking, you should avoid having a catchall route. All types of unknown requests will hit your fallback backend, opening the door for malicious users to test and scan it. From a security perspective, you are safer without this because you cut any traffic that you don’t explicitly declare. Remove /__catchall.
- Recommendation
-
5.1.6Avoid using multiple write methods in endpoint definitions. - Severity
- MEDIUM
- Rationale
- You are doing a distributed transaction when you declare multiple unsafe methods (like POST) in a single endpoint. You don’t have any rollback or fail-safe mechanism in the gateway, and you can only hope for the best.
- Recommendation
-
5.1.7Avoid using sequential proxy. - Severity
- MEDIUM
- Rationale
- Using sequential calls is considered an anti-pattern because when you make a network service dependent on the other, you are increasing the latency, decreasing the performance, and augmenting the error rate. Avoid sequential proxy
5.2 Proxy pipe
Recommendations for proxy pipe configurations and best practices
- Recommendation
-
5.2.1Ensure all endpoints have at least one backend for proper functionality. - Severity
- CRITICAL
- Rationale
- Having at least one backend per endpoint ensures that the endpoint is functional and can handle incoming requests. Add a backend
- Recommendation
-
5.2.2Benefit from the backend for frontend pattern capabilities - Severity
- LOW
- Rationale
- All of your endpoints are connected to a single backend. Creating endpoints that connect simultaneously to several backends and aggregate the information, increases the speed and quality of service you deliver to end-users.
- Recommendation
-
5.2.3Avoid coupling clients by overusing no-op encoding. - Severity
- LOW
- Rationale
- Abusing no-op encoding can lead to client coupling, which can negatively impact scalability and maintainability. It is recommended to use a different encoding for your clients and endpoints other than no-op.
6. Event Driven Gateway
Recommendations for implementations of event-driven gateway and async agents that can lead to problems.
6.1 Async agents
Recommendations for async agents configuration and deployment issues
- Recommendation
-
6.1.1Ensure Async Agents do not start sequentially to avoid overloading the system. (+10 agents) - Severity
- LOW
- Rationale
- Starting too many async agents one after the other can cause delays during startup. Ensure that async agents are started asynchronoulsy by disabling sequential start.
7. Deprecated components
Components that are unsupported or discontinued. Their usage is descouraged as they will be removed in new versions and they do not receive security updates.
7.1 Deprecated plugins
Plugins that even might be functional, they are marked as deprecated and do not receive security patches. Upgrade to their alternative when available.
- Recommendation
-
7.1.1Virtual Host is now a native component - Severity
- HIGH
- Rationale
- Avoid using deprecated plugin virtualhost. and use its native counterpart instead See upgrading from plugin to upgrade to the new virtualhost.
- Recommendation
-
7.1.2Static Filesystem is now a native component - Severity
- HIGH
- Rationale
- Avoid using deprecated plugin static-filesystem and use its native counterpart instead. See upgrading from plugin to upgrade to the new static-filesystem..
- Recommendation
-
7.1.3Basic-Auth is now a native component - Severity
- HIGH
- Rationale
- Avoid using deprecated plugin basic-auth and use its native counterpart instead. Please move your configuration to the namespace auth/basic to use the new component. See basic authentication documentation.
- Recommendation
-
7.1.4Wildcard is now a native component - Severity
- HIGH
- Rationale
- Avoid using deprecated plugin wildcard. and use its native counterpart instead See upgrading from plugin to upgrade to the new Wildcard.
- Recommendation
-
7.1.5HTTP PROXY is now a native component - Severity
- HIGH
- Rationale
- Avoid using deprecated plugin http-proxy and use its native counterpart instead. See upgrading from plugin to upgrade to the new options.
- Recommendation
-
7.1.6Static Filesystem is now a native component - Severity
- HIGH
- Rationale
- Avoid using deprecated plugin static-filesystem and use its native counterpart instead. See upgrading from plugin to upgrade to the new static-filesystem.
- Recommendation
-
7.1.7No-redirect plugin is now a native component - Severity
- HIGH
- Rationale
- Avoid using deprecated plugin no-redirect and use its native counterpart instead. See upgrading from plugin to upgrade to the new options.
- Recommendation
-
7.1.8content-replacer plugin is now a native component - Severity
- HIGH
- Rationale
- Avoid using deprecated plugin content-replacer and use its native counterpart instead. See upgrading from plugin to upgrade to the new options.
- Recommendation
-
7.1.9response-schema-validator plugin is now a native component - Severity
- HIGH
- Rationale
- Avoid using deprecated plugin response-schema-validator and use its native counterpart instead. See upgrading from plugin to upgrade to the new options.
7.2 Deprecated namespaces
Namespaces that even might be functional, they are marked as deprecated and do not receive security patches. Upgrade to their alternative when available.
- Recommendation
-
7.2.1Unsupported namespace telemetry/ganalytics - Severity
- HIGH
- Rationale
- Avoid using deprecated component telemetry/ganalytics. Upgrade to OpenTelemetry.
- Recommendation
-
7.2.2Unsupported namespace telemetry/instana - Severity
- HIGH
- Rationale
- Avoid using deprecated component telemetry/instana. Upgrade to OpenTelemetry.
- Recommendation
-
7.2.3Deprecated component telemetry/opencensus - Severity
- HIGH
- Rationale
- Avoid using deprecated component telemetry/opencensus. Upgrade to OpenTelemetry.
7.3 Deprecated configuration options
Configuration options that will become unavailable in future versions.
- Recommendation
-
7.3.1Add missing level `keys` - Severity
- MEDIUM
- Rationale
- Avoid using
private_keyandpublic_keydirectly undertlsand place them inside thekeysarray. See TLS Server Settings
