Document updated on May 16, 2024
Wildcard Endpoints
The wildcard functionality allows you to declare endpoints that have many implicit paths in their backend. Instead of declaring all possible routes one by one, you can create one or more endpoints that will respond to a path pattern instead. The gateway then forwards all routes starting with the configured path to the backend(s).
For instance, you can declare an endpoint /foo/* that forwards all traffic starting with /foo/ to a specific backend. When a user calls /foo/bar or /foo/bar/vaz, the request is processed by the same endpoint and backends.
Since paths are implicit, KrakenD does not know if a request is valid or not beyond checking that the pattern is correct, or checking additional components you might add. Therefore, everything it can do is to “hope for the best” before routing the request, and it is the responsibility of the backend to determine if the path is valid.
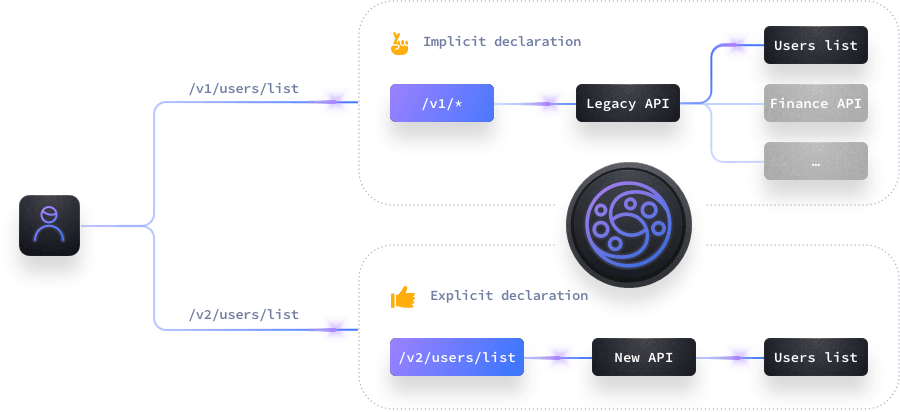
The wildcard functionality is a good candidate when you are in a migration scenario and you need to expose a lot of endpoints quickly. However, it would be best to transition to an explicit declaration instead, and you should aim for it if security is a concern.
Wildcard configuration
To enable wildcards, you only need to write a string ending in /* in the’ endpoint’ path. Then, the receiving backend will automatically append the remaining request to its url_pattern. For instance, given the following configuration:
{
"endpoint": "/v1/*",
"backend": [{
"host": ["http://legacy-api"],
"url_pattern": "/"
}]
}
When requesting to http://krakend/v1/hello, you get a request to your backend ashttp://legacy-api/hello. Notice that you don’t need to write any asterisk in the url_pattern.
The wildcard applies to the path only. If you want to use multiple methods (GET, PUT, POST, etc.), you still need to create an entry per method as in any other KrakenD endpoint.
Wildcard Limitations
Make sure to declare wildcards per the following rules:
- You cannot use multiple asterisks (e.g.:
/v1/*/foo/*). Instead, use{placeholders}. E.g.,/v1/{service}/foo/*. - You cannot route all traffic on the root level (e.g.,
"endpoint": "/*"). Therefore, you must declare at least one directory level before placing the wildcard. See the Catch-All endpoint for such uses. - You cannot declare colliding paths. For instance if you have an endpoint
/v1/fooyou cannot create a wildcard/v1/*(although you can do this with the old plugin, see documentation below) - You cannot have an endpoint that starts with a
{variable}and ends with*, like/{foo}/bar/*, except when there is one level alone/{foo}/*.
Examples of valid paths:
/a/b/c/*/a/*/{var}/*(when alone)
Examples of invalid paths:
/abc*(doesn’t end in/*)/*(forwards all traffic, use Catch-All instead)/*/a/*(multiple uses of*)/{foo}/bar/*(starts with variable)/{foo}/{bar}/*(starts with variable)
disable_redirect_fixed_path, which is the underlying reason for unhandled collisions.As you can see, combining the wildcard with endpoint variables is possible. For instance, you could have the following paths configured:
{
"endpoints": [
{
"endpoint": "/v1/{service}/*",
"backend": [{
"url_pattern": "/v1/{service}/"
}]
},
{
"endpoint": "/{owmamma}/*",
"backend": [{
"url_pattern": "/{owmamma}/"
}]
}
]
}
Upgrading from the old wildcard plugin (before v2.3)
If you used Wildcards before EE v2.3, eliminate now all entries referring to plugins. This means:
- If you don’t use additional plugins, you can get rid of the
pluginentry in the root level. - You can delete all
plugin/http-serverobjects if they only use the wildcard - You can delete any
wildcardobject in the configuration - You can delete all
plugin/http-clientwith an insiderwildcardentry. - You can delete all
"X-Krakend-Wildcard"entries ininput_headers.
For instance, if you had this configuration:
{
"version": 3,
"port": 8080,
"plugin": {
"pattern":".so",
"folder": "/opt/krakend/plugins/"
},
"extra_config": {
"plugin/http-server": {
"name": [ "wildcard" ],
"wildcard": {
"endpoints": {
"/__wildcard/foo": [ "/foo" ],
"/__wildcard/legacy": [ "/v1" ]
}
}
}
},
"endpoints": [
{
"endpoint": "/__wildcard/foo",
"input_headers": [ "X-Krakend-Wildcard" ],
"backend": [
{
"host": [ "http://localhost:8080" ],
"url_pattern": "/__debug/foo",
"extra_config": {
"plugin/http-client": {
"name": "wildcard"
}
}
}
]
},
{
"endpoint": "/__wildcard/legacy",
"input_headers": [ "X-Krakend-Wildcard" ],
"backend": [
{
"host": [ "http://localhost:8080" ],
"url_pattern": "/__debug/legacy",
"extra_config": {
"plugin/http-client": {
"name": "wildcard"
}
}
}
]
}
]
}Since EE 2.3, it has become:
{
"version": 3,
"port": 8080,
"endpoints": [
{
"endpoint": "/foo/*",
"backend": [
{
"host": [ "http://localhost:8080" ],
"url_pattern": "/__debug/"
}
]
},
{
"endpoint": "/v1/*",
"backend": [
{
"host": [ "http://localhost:8080" ],
"url_pattern": "/__debug/"
}
]
}
]
}
